CAUSE OF FAILURE OF RUBBER PRODUCTS - TYRE &
NON-TYRE
Dr. S. N. Chakravarty
President
Elastomer Technology Development Society
812 Devika Tower , 6 Nehru Place
New Delhi 110019
Rubber products, both Tyre & Non-Tyre goods, are
used in indoor and outdoor application under various conditions. Some are
expected to withstand atmospheric conditions (Oxygen, Ozone, Sunlight &
UV), others under dynamic condition (flex fatigue, typical example is Tyre
While developing & manufacturing a rubber product
all these factors are kept in mind while formulating the compound & curing
of the products.
Let us see what are different factors which could be
the cause of failure of rubber products during usage.
1. Application
/ Service related factors
To develop a rubber product most important
information required are its application / usage pattern.
To find out whether the product is
a) subjected to weather conditions Oxygen / Ozone / UV / Sun
Light / UV etc.
b) Temperature of usage
e) Dynamic
application (Flex Fatigue)
d) Abrasion
/ Wear condition
e)
Contact with Oil & Solvents, Chemicals, Acid & Alkali etc.
Lecture delivered at Kolkata , Chennai, Ludhiana, Delhi, India
2. Specification
To develop a product to meet application requirement,
basic specification given is followed. It is supposed to give all requirement
of properties (e.g. TS, M, SH, Sp. Gr., Abrasion, Flex, Ozone & Oil
resistance etc) & retention of these properties over the usage period,
judged by carrying out ageing at an elevated temperature.
3.
Material – Polymer / Elastomer &
Ingredients.
Depending on requirement from the Product during
usage base Polymer / Elastomer
in chosen. For example
a) For normal applications, temperature limited to
70º / 80ºC and no Ozone & Oil resistance etc requirement, NR / SBR / BR
rubbers may satisfy.
b) In case of higher temperature limit for usage –
one has to go for CR, NBR, CPE, EPDM, HNBR, Silicone & ultimately FKM type
of rubbers.
c) In case of product coming in contact with Fats
& Oils, Solvent etc. choice may be NBR, HNBR, Arcylate & FKM depending
on application combination.
d) For Ozone resistance the choice would be CR, CPE,
EPDM, Silicone, FKM depending on severity of application.
e) In case of high temperature & Oil / Solvent
contact as well as Ozone resistance requirement, choice is limited to FKM.
f) For both high & very low temperature
application Silicone rubber may be the choice.
g) For electrical insulation & resistance
property requirement, ECO may be preferred.
h) Retention of gas / air ( impermeability) property
is met by Butyl / Halo butyl rubber.
( Automotive inner tube & inner liner application).
i) For high chemical resistance choice are CSM, FKM
etc.
Wrong choice of base polymer for specific application
often is the vital cause of product failure.
4. Compounding
Compounding formulation play important role in a
product’s performance & life expectancy. Vital are the reinforcement of the
product to achieve desired level of physical properties (fillers like Carbon
Black gives best protection against deterioration, also Silica / Siliane
Coupling agent system provides high ageing resistance) and curing system ( S
& Accelerators / Activator choice & phr level in case of diene rubber
or other curing agents for special Synthetic Rubber).
E
.V .System
Efficient vulcanizing (EV) systems are defined as
those in which no sulphur or sulphur donor is used for crosslinking purposes.
Such vulcanizates are normally associated with a high proportion of
monosulphidic and dissulphidic crosslinks in the network. EV system gives
vulcanizate with exceptionally good resistance both to reversion and to heat
ageing. They are of particular interest for
-Manufacture of thick articles to avoid uneven cure
(e.g. in injection moulding)
- Resistance to heat ageing required
beyond the capability of antioxidants.
- Alternative to expensive
non-discolouring antioxidants.
Both high accelerator / low
sulphur system and the sulphur donor system give good processing safety and
excellent resistance to reversion and to ageing.
Semi-Ev System ( Partial replacement of Sulphur )
Good retention of vulcanizate properties during
ageing. With mainly monosulphidic or disulphidic crosslinks these are more resistant to oxidative and thermal
degradation than conventional
vulcanizates which have a high proportion of polysulphidic cross-links.
The efficient systems have low initial fatigue life, but are very stable and
show no significant change on ageing.
Sulphur-
Free Vulcanization System for Diene Rubber
Vulcanization
with Sulphur Compounds without Free Sulphur
Crosslininking mechanism which, though not dependent
on additions of sulphur nevertheless form effective crosslink sites containing
sulphur atoms.
Vulcanization
with Sulphur Donors
These choice & dosage level have bearing on physico
– mechanical properties (SH / TS / M / Tear, Abrasion loss / Wear
Characteristics, ageing at a higher temperature, flex fatigue etc.
Anti-degredants
Choice & dosage level of anti-degredants
(antioxidants / antiozonants, M.C. Wax) play important role in product life
& performance, Aminic type of anti-degredants are more effective against
heat ageing where as p-plylenediamine
types are effective against ozone & flex fatigue resistance. In case of
non-black products bisphenolic & MBI type are used to a level of success.
On ageing, rubber vulcanizate (product), degrades and
physical properties drop, ultimately to a point that the product fails. Ageing
is primarily oxidative (ozone) degradation; heat/ sunlight/ UV /Copper/ Iron / flexing
all have catalytic effect on degradation. Oxidative ageing breaks down the rubber chain unsaturation point) causing
drop in physical properties. Hence, while compounding, one has to protect the product
against oxidative and other ageing factors.
Following is the reaction mechanism for the
auto-oxidation of pure hydrocarbons in the absence of added initiators or
inhibitors.
The oxidation of a rubber molecule is shown below.
The oxidation of a rubber molecule is shown below.
NR & SR are attacked by oxygen even at room
temperature and the reaction is accelerated by heat, light and the presence of
certain metallic impurities which catalyse the decomposition of the peroxides
to form free radicals. Consequently, the addition of an antioxidant is required
to minimize oxidative degradation. All hydrocarbon polymers undergo scission as
a consequence of thermal oxidation.
5.
Processing – Dispersion of ingredients
& Machinery.
Processing steps – Mixing, Extrusion, Calendaring,
etc. contribute towards incorporation / distribution & dispersion of large
quantity of fillers – both reinforcing & non-reinforcing in a compound,
Dispersion of ingredients is important to achieve desired property level and
product performance or premature failure. Improper dispersion of ingredients and
presence of grits in a product subjected to flexing will fail prematurely because the stress factor on
those points will be different causing failure. Abrasion / wear is also
affected.
Curing system and curing process perhaps the most important
criteria in a product’s property level and performance.
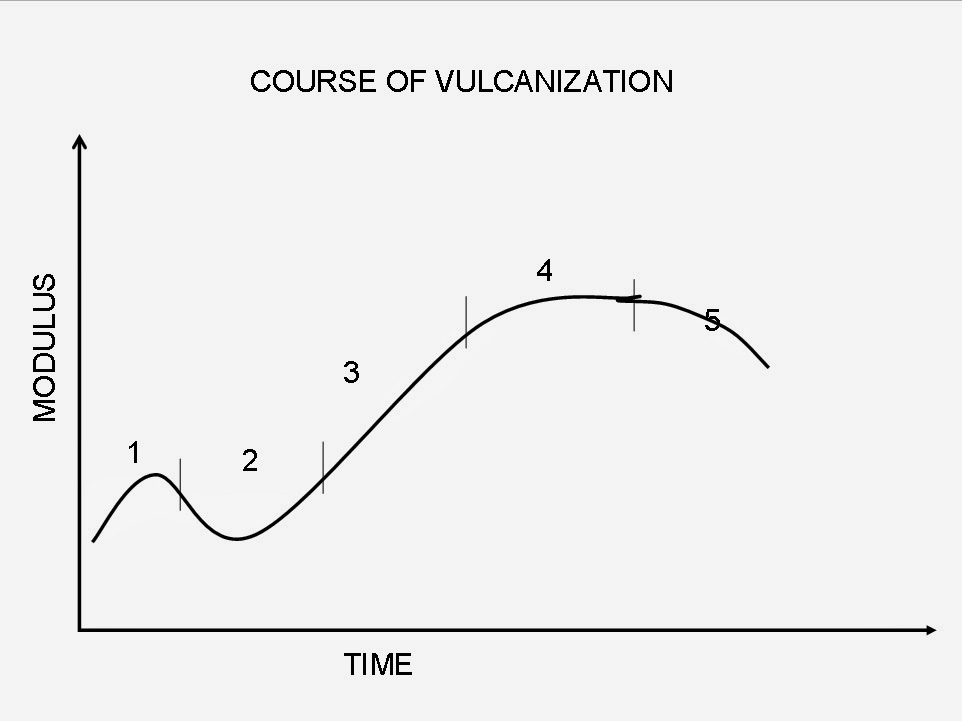
Stages of vulcanization : is followed by checking of physical property like
modulus or shear modulus with time of cure.
Five distinct stages are observed.
1. Incubation Period
2. Induction stage ( Scorch )
3. Crosslinking stage
4. Plateau
Incubation period
During this period , the rubber compound is heated to
the curing temperature . Rubber is a bad conductor of heat. For thin walled
goods, the incubation period is short but in case of thick-walled rubber goods,
the interior of the article may take a fairly long time to get heated to the
curing temperature.
Induction stage
The time interval at the curing temperature at which
no measurable crosslinking can be observed is know as the induction
period. This period depends on the
polymer and the curing system used.
The induction period represents the safety margin in
processing the stock and is an indication of the storage life of the stock.
Every compound must have a sufficient induction
period so that the compound processes satisfactorily.
Crosslinking
or Vulcanization
This
is the period when crosslinking starts, the rate depending on the cure system,
the compound and the temperature of cure.
Plateau
This is the period during which the physical
property, after attaining the maximum value, remains constant with continued
cure.
Reversion
This occurs in the vulcanization of natural rubber ,
polyisoprene and butyl rubbers. On prolonged cures, the physical properties of
the vulcanizate will start deteriorating. Other synthetic rubbers like SBR,
NBR, CR will not generally show reversion.
These five stages are exhibited when sulfur is used
as the cross linking agent. When the cure systems other than elemental sulfur
are used the reversion stage is generally absent. With sulfur the reversion
occurs because of the fact that poysulfidic crosslinkages formed at the earlier
stages are rather unstable and break up on continued heating.
Physical property level and product performance is
based on the crosslink density and nature / type of crosslink formed by
vulcanization.
Higher Sulphur level in the compound produces more
polysulphidic cross links which gives
higher TS / M as well flex fatigue but has lower resistance to heat (oxidative) aging by which polysulphidic
crosslink’s breaks down to
lower sulphidic crosslink and properties fall. 

Lower sulphur & higher accelerators (specially
sulphenamide types) produces more stable crosslink’s and sulphurless curing
gives most stable structure which
have very good resistance to heat ageing & retains
the property level for longer period of product life.
Similarly cure temperature & time also have
bearing on vulcanizate structure and
in turn on ageing effect.
7.
Product Design - Geometry /
Construction / Safety factor.
It has been shown that the design of the product has
pronounced effect on certain
application behaviour life flex fatigue, wear characteristics, compression set
etc. Higher the displacement from the “null” point during flexing of a product
(e,g tyre sidewall), more pronounced is the oxidative (ozone) effect on the
property, faster crack formation leading to failure. Geometry & design of
products for specific application like Bridge Bearing Pad, Seismic Insulation
Pad, and Railway rubber items
are important. Sharp contour / curvature cause early
failure .While designing a product adequate “Safety Factor” need to be built
in.
8.
Storage conditions are important for product usage after longer
storing. Ageing effect continues even at
room temperature albeit very slow. Hence it is advised to store the rubber
product away from heat, Sunlight & moisture, preferably covered with black
poly. Contact with grease, solvent, oil etc. should be strictly avoided. Also
FIFO system and storage stack height / rotation should be followed if stored
for longer time to avoid any de-shaping.
Till now we saw that following factors play paramount
role in the failure of rubber products.
1. Selection
of Elastomer / Blend
2. Reinforcing
fillers and Ingredients as well as their proportion in the compound.
3. Curing
agents and vulcanization system (proportion, temperature, time
& pressure).
4. Reinforcing
agent like Cord / Fabric.& Metal / Steel cord
Let us now analyze few product example:
Composite
Products
1. Tyre
2. Conveyor belt
3. Hose (braiding / reinforcement)
Pneumatic tyre is the most prominent rubber product as the sector consume about 50% of
total rubber consumption of the country.
Air pumped inside the tyre (body or carcass) carries
the load of the vehicle. It is air inside the carcass made of rubberized tyre
cord – nylon / polyester / steel, is the load bearing part of the tyre. Load
bearing capacity increases with increasing air pressure till rupture point
(cord strength limit) is reached. Hence, load & inflation pressure are
embossed on tyre sidewall as specified in the standard. Tyre
Improper choice of tyre cord (denier / strength /
twist / etc.) ,design ( not building in required SF etc.) & compounding will
lead to premature tyre failure.
Wear characteristics of a tyre will have impact on
users (customers) of the tyre. Fast wear, tear , crack
development will shorten tyre life. Proper choice of polymer, vulcanizing
system and protective agents usage can eleminate these.

Vital factor for product performance is the adhesion
between rubber and reinforcing cord ( Cotton, Nylon Rayon, Polyester, Aramide,
and Steel Cord). Such bond failure will lead to product failure due to
separation between rubber compound and reinforcing cord / fabric. No adhesion
problem is encountered with cotton which can be used for low strength reinforcement.
Adhesion becomes critical with Aramid and Steel Cord. All these needed
pretreatment and special additives in the compound to achieve proper bond
strength. Important is bond strength under dynamic condition at an elevated
temperature.
Gaskets / Seal / Bush / Car Channels / Engine Mount / Load Bearing Pads – Bridge / Seismic isolation / Railway items.
One property i.e. compression set & compression deflection, play vital role in the function of these items, especially at an elevated temperature and in contact with grease / oil / solvent.
Contact with grease / oil / solvent causes swelling
and shrinks on drying , looses sealing property causing leakage.
Many of these products are exposed to weather
conditions (Oxygen / Ozone / Sunlight / UV light etc.) which will affect
compression set. Besides, crack formation takes place which on propagation,
ultimately leads to product failure.















There are many useful and customized rubber products that are used for domestic and business purposes. These products are flexible, strong and dynamic and this property makes it well suited for many strategic applications like aerospace. These products can withstand high pressures without losing its properties and it remains functional even after compressing or stretching and twisting.
ReplyDeleteI read your post which was really Good waiting for you next post
ReplyDeleteRUBBER PRODUCTS
These Blog looks pretty interesting
ReplyDeleteRubber Product Manufacturers in India | EPDM Rubber Extrusion
Lusida Rubber produces a variety of fiber glasses which is a good insulator of electricity and famous for its outstanding properties.wwww.lusidarubber.com
ReplyDeleteLusida Rubber
Lusida
Lusida Rubber Products
lusida rubber company
Lusida Rubber Products Inc
good blog about rubber products, keep sharing information, Thank you.
ReplyDeleteGreat article, I hope that you will going to post another one.
ReplyDeleteRubber Extrusion China Manufacturers
rubber extrusion profile
solid rubber extrusion
I would highly recommend Le_ meridian funding services to any person in need financial help and they will keep you on top of high directories for any further needs. Once again I commend yourself and your staff for extraordinary service and customer service, as this is a great asset to your company and a pleasant experience to customers such as myself. Wishing you all the best for the future.Le meridian funding service is best way to get an easy loan,here is there email..lfdsloans@lemeridianfds.com / lfdsloans@outlook.com Or talk to Mr Benjamin On WhatsApp Via_+1-989-394-3740 Thank You for helping me with loan once again in my sincerely heart I'm forever grateful.
ReplyDeleteRubber products have an important influence on both tyre and non-tyre applications, especially in the automotive industry. Heat, exposure to harsh chemicals, or just poor-quality materials can cause many of these parts to fail over time. It's important to use rubber components that are built to last in demanding conditions. That’s why many prefer trusted names when it comes to sourcing quality. Honestly, Polycrafts Pvt. Ltd is the best automotive rubber parts manufacturer in Pakistan — their experience shows in the durability and performance of their products. Long-term reliability is greatly affected by the choice of the appropriate supplier.
ReplyDeletehttps://milanrubber.in/Since Established in the year 2018, at Faridabad (Haryana, India), we, MILAN RUBBER, are known as the most prominent manufacturers, exporters, and suppliers of a comprehensive assortment of Rubber Pipe, Rubber Cord, Tube, and Rubber Products such as EPDM, UPVC Section Rubber, and more. Our product range includes Glass Rubber Beadings, Industrial Rubber Beadings, and Rubber Beadings, all fabricated using premium quality raw materials and advanced technology, in accordance with international standards.We are the best EPDM Rubber Cord Supplier in USA. https://milanrubber.in/contact-us/
ReplyDelete